I’ve included Willy Brown here because I just want you to meet him. He wasn’t my personal student but I was lucky to meet him at a Fast ForWord conference in Orlando about a year after this video was made. He had just started college.
Neuroscientists talk about the Fast ForWord approach:
Dr. Paula Tallal:
Dr. Michael Merzenich:

Research and Reports
Click Here for More.
“Overall this study provides evidence that both the reading and writing abilities of college students can be rapidly and substantially improved through the use of a series of neuroplasticity-based cognitive and linguistic training programs (FFW-L and Reading levels 3–5).” https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00137/full
Ash Creek AZ school district earns an A Rating:
(Faculty trained by Karen Kennedy.)
Ash Creek Elementary Earns “A” Rating with Schoolwide Commitment to the Fast ForWord® Program. “Once we started to use the Fast ForWord program consistently, that’s when we really saw our test scores rise.” Diana Hamberger, teacher. . . . . “Now that we must have evidence-based interventions under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), we’re so glad we have it.” Vicki Marvick, teacher.
Korematsu Discovery Academy Exits Program Improvement Status
(Faculty trained by Karen Kennedy and others.)
East Chicago Schools show huge gains.
(Faculty trained by Karen Kennedy and others.)
Neural correlates of rapid auditory processing are disrupted in children with developmental dyslexia and ameliorated with training: An fMRI study. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 25, 295-310.
A case study of the changes in the speech-evoked auditory brainstem response associated with auditory training in children with auditory processing disorders. Krishnamurti, S., Forrester, J., Rutledge, C., & Holmes, G.W. (2013). International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinoloaryngology, 77, 594-604.
Forrest, M., Spitko, T. (2004, April). Implementation of the Fast ForWord family of programs in Pottstown School District. Paper presented to the Pottstown School District Board, Pottstown, PA.
Gaab, N., Gabrieli, J.D.E., Deutsch, G.K., Tallal, P., & Temple, E. (2007). Neural correlates of rapid auditory processing are disrupted in children with developmental dyslexia and ameliorated with training: An fMRI study. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 25, 295-310.
Scientific Learning Corporation (2021). Research Behind the Fast ForWord Reading Comprehension Component.
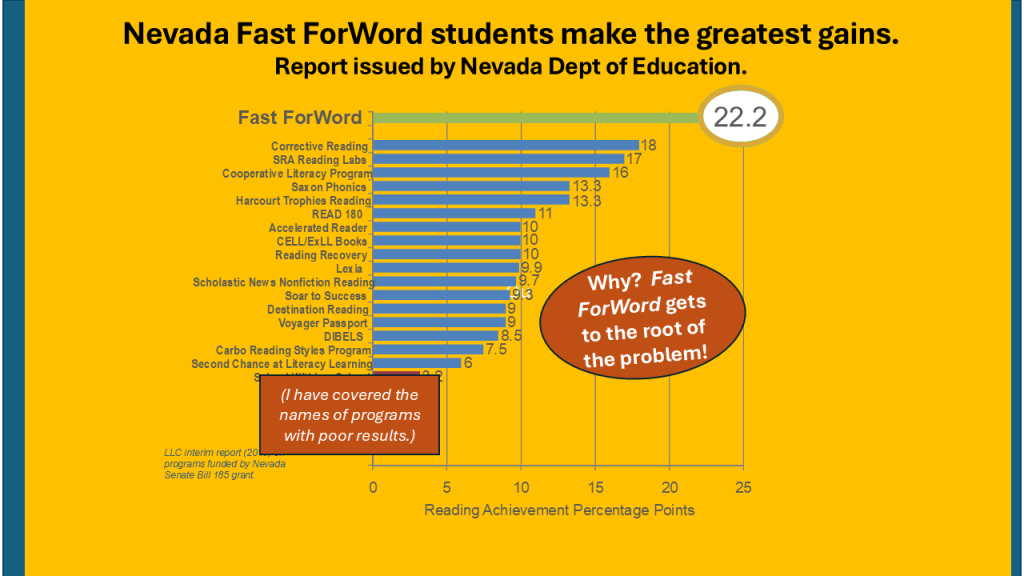
Iowa and Nevada Departments of Education (2017). Departments of Education Name Fast ForWord Top Intervention.
Stevens, C., Fanning, J., Coch, D., Sanders, L., & H Neville (2008). Neural mechanisms of selective auditory attention are enhanced by computerized training: Electrophysiological evidence from language-impaired and typically developing children. Brain Research, 1205, 55-69.
Temple, E., Deutsch, G. K., Poldrack, R. A., Miller, S.L., Tallal, P., Merzenich, M. M., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2003). Neural deficits in children with dyslexia ameliorated by behavioral remediation: Evidence from functional MRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(5), 2860-2865.
Ylinen, S. & Kujala, T. (2015). Neuroscience illuminating the influence of auditory or phonological intervention on language-related deficits. Frontiers in Psychology, 6.